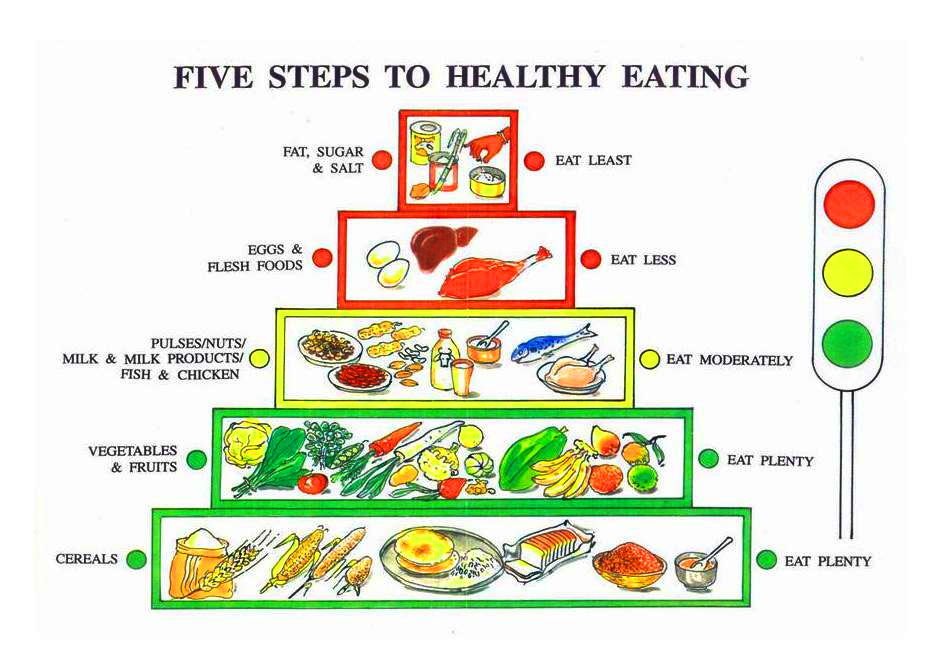
Geriatrics (or geriatric medicine) involves preventing, diagnosing, and treating health problems in elders.
A geriatrician, or geriatric physician, works to promote health in the elderly while preventing and treating diseases prone to elders. Their work includes: –
- Multiple diseases and conditions
- Chronic diseases and conditions
- Symptoms from multiple medications
Doctors who specialize in geriatric medicine are skilled at caring for elderly patients. They are first trained and board certified in either family medicine or internal medicine. Geriatricians then have additional training in geriatric medicine.
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) responded to the challenges of population ageing in India by starting a weekly clinical service in 1993 with focus on establishment of service, human resource development and research. The weekly outpatient service was upgraded to a daily service in August 2010 and an academic department in January 2012 as a distinct specialty of Medicine. The first batch of MD students was admitted in January 2012 and the Geriatric Medicine Ward came to existence in July 2012.
Physicians who are experts in caring for the elderly consider their patients as a whole. For example, geriatricians examine a patient’s medical history to determine how earlier illnesses or conditions interact to affect current health; they determine whether their patients have required social support from family, friends, and the community; and they inquire about and make recommendations for living conditions. They also assess a patient’s ability to perform activities of daily living and make recommendations to help older patients and their families adjust to and manage changes that come with aging.

“Geriatricians work closely with other physicians to ensure their patients get comprehensive care,” says geriatrician John A. Heath, MD, AGSF. “For example,” adds Dr. Heath, “a geriatrician often partners with a urologist to help patients with incontinence, a neurologist to help patients with memory problems, and an ear specialist for patients with hearing and balance problems. Most importantly,” Dr. Heath emphasizes, “geriatricians work with a team of professionals who are trained in and dedicated to eldercare.”
Geriatrics teams include health professionals with advanced training, certifications, and expertise in geriatrics, including:
- Nurses
- Social workers and care managers
- Pharmacists
- Physiotherapists
- Nutritionists
- Occupational therapists
- Mental health professionals
As leader of the geriatrics team, the geriatrician examines records from each member of the geriatrics team to regulate the best possible treatment and develop care plans that meet the needs of the old age patients.
Who Should See a Geriatrician?
Although most people who need geriatric care tend to be age 75 or older, patients should see a geriatrician if they:
- Cannot perform regular activities of daily living such as bathing, dressing, and eating etc.
- Are becoming fragile or forgetful.
- Have more than 1 worsening condition or disease that might require a change in living situation
- Seek care to control symptoms (palliative care) and manage multiple chronic conditions in advanced stages
- Fear they are becoming a burden to family and friends
Data from the American Geriatrics Society show that older people who receive care from a geriatrician do better at maintaining their ability to engage in normal activities and spend less time in hospitals and nursing homes.